Highlights:
- Demand for rechargeable batteries has skyrocketed, and investment in battery research has increased in turn
- Significant technical challenges face the industry, ranging from increasing specific energy to thermal stability, battery life extension and disposal of spent materials
- Discover how Maplesoft helped ControlWorks develop a Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) testing system for a Battery Management System
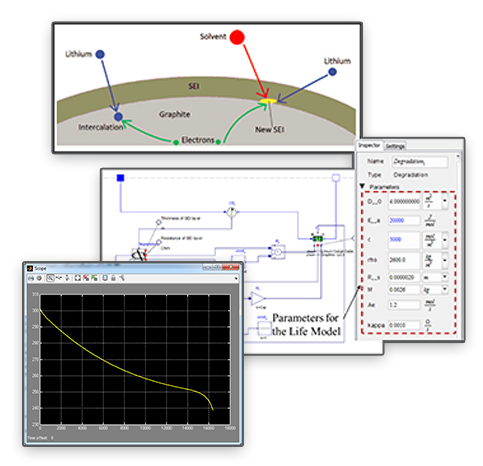
The explosion in the use of electronic devices, electrified vehicles and decentralized power utilities (e.g. smart grids) has driven demand for rechargeable batteries, creating a thriving and growing market. Current projections indicate that the global market for rechargeable batteries will be approximately $60 billion in 2015, growing at around 9% per year. This has led many of the major electronics companies to enter the market, with offerings targeting a range of applications: from small and light-weight for hand-held devices to batteries the size of shipping containers for utilities. It has also led to a significant increase in research investment into battery technologies to address many of the technical challenges facing this industry, ranging from increasing specific energy (the amount of charge a cell can hold per kg weight) to thermal stability, battery life extension, and final disposal of spent materials at the end of a battery's life.
In this paper, we will focus on one area of development in the context of a project recently carried out by Maplesoft and its partner, ControlWorks Inc, of South Korea. Specifically, we will cover the development of a Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) testing system for the Battery Management Systems (BMS) used in one of our client's larger electrical energy storage products, targeting the Smart Grid and UPS markets.


