
The modern automobile is a complex collection of mechanical, chemical, electrical, hydraulic, and other types of physical systems, all of which have strong connections to mathematics.
During the 19th century, scientists developed ways to mathematically model energy, and through these models they were able to build the practical engines that led to the modern car.
Otto (4 stroke) Cycle:

Nikolaus Otto (German, 1832-1891), a scientist, developed a version of the internal combustion engine that was efficient enough for practical automobiles. Today, his Otto thermodynamic cycle is the scientific foundation for most gas-powered cars.
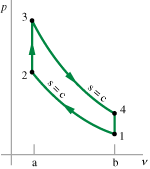
1 » 2 Intake stroke (isentropic compression)
2 » 3 Compression stroke (constant volume heating)
3 » 4 Power stroke (isentropic expansion)
4 » 1 Exhaust stroke (constant volume cooling)
The maximum efficiency for engines that use this cycle is given by: 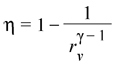
where, 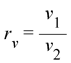 is the compression ratio and
is the compression ratio and 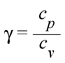 is the heat capacity ratio.
is the heat capacity ratio.


