What's New in Maple 2022
From simple operations to cutting-edge research, the new features in Maple 2022 will make your work easier.
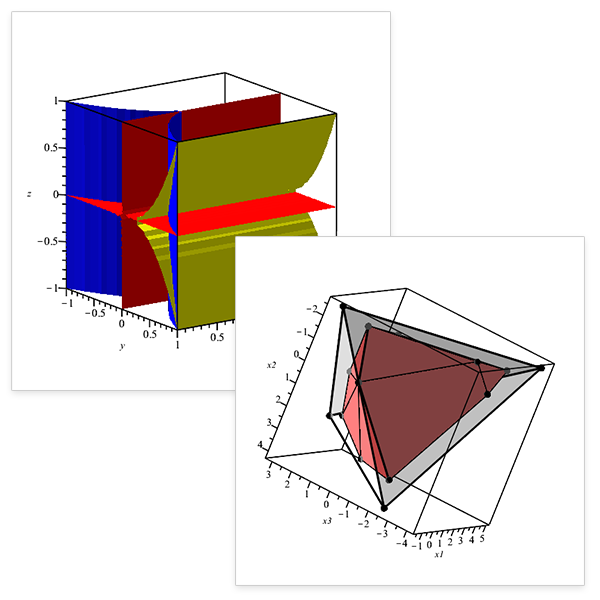
Math, Math, and More Math
Maple 2022 solves more math problems, in more areas, than ever before. Of course.
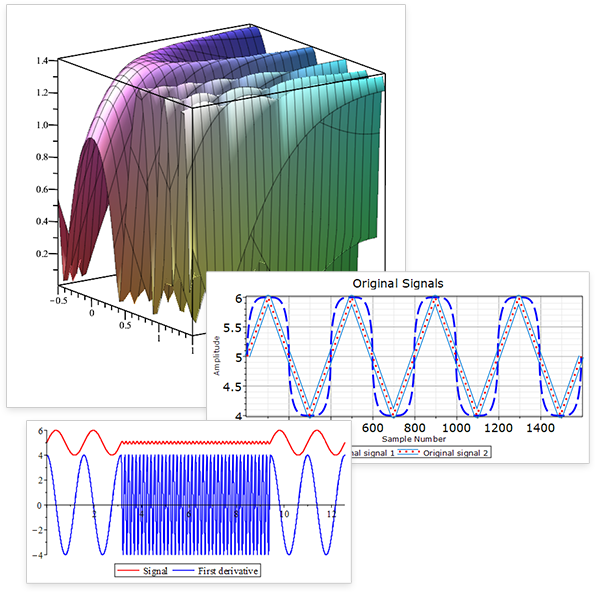
Separate Signal from Noise
New signal processing tools let you create, combine, and analyze signals in more ways, more efficiently.
Wear Your Tux
Working with formal power series is significantly improved in Maple 2022, offering more, better solutions than ever.
Understanding the Universe
Maple’s state-of-the-art environment for algebraic computations in physics offers enhanced tools for tackling problems in particle physics, general relativity, and more.
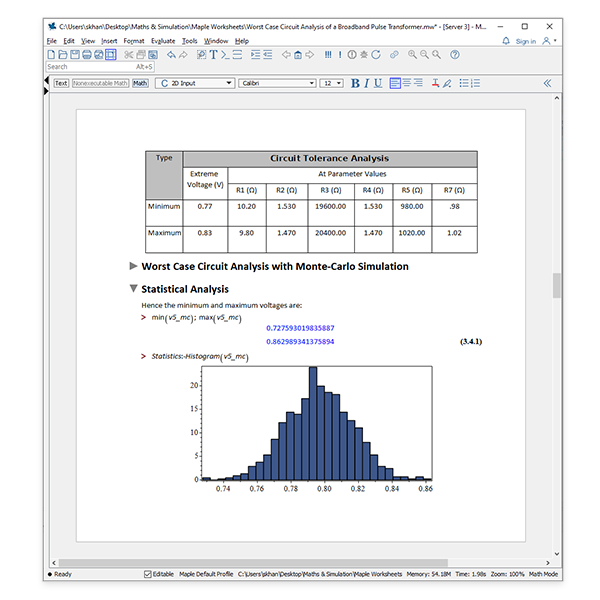
Prepare for Print
Preparing documents for printing and PDF export is now easier than ever with a new print layout mode.
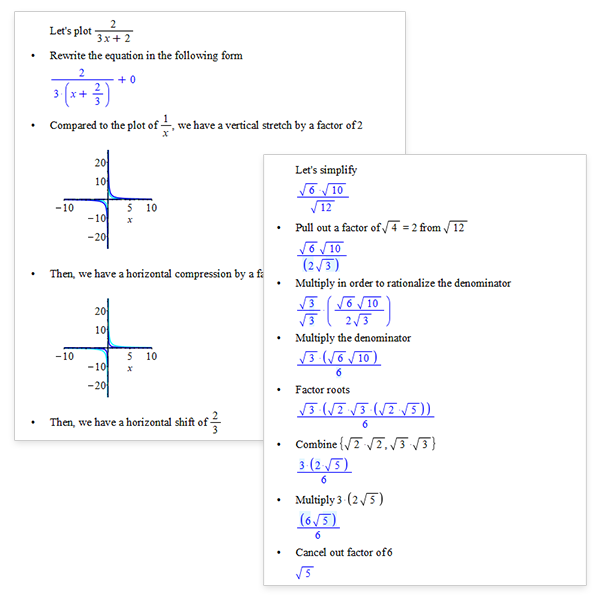
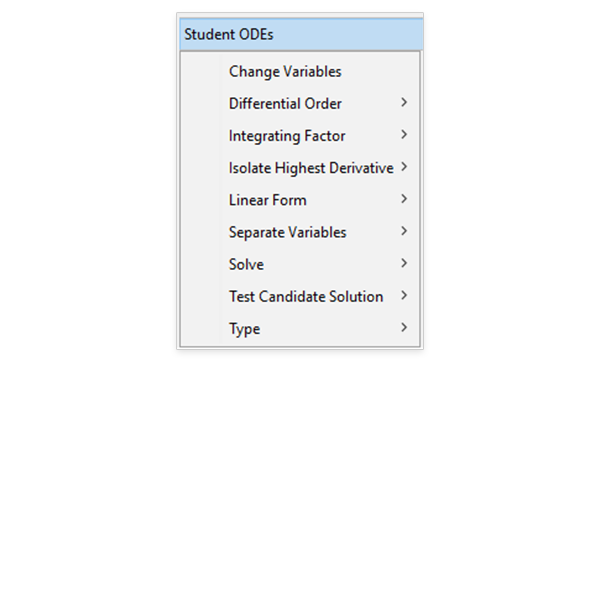
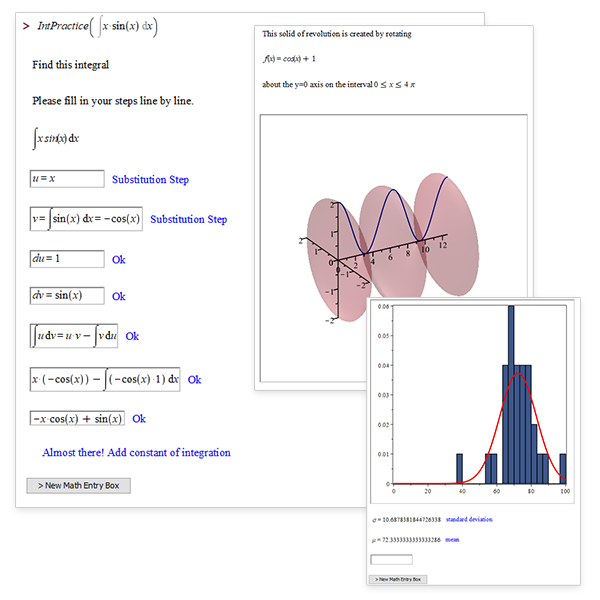
Break It Down
Maple 2022 helps students practice solving more problems on their own with step-by-step solution tools for expression simplification and curve sketching.
Units Matter
New and improved tools for calculating and visualizing values involving units makes keeping track of your units easier than ever.
Creating and Sharing Content
Maple 2022 greatly extends the tools for programmatically creating documents and interactive applications for Maple and Maple Learn.
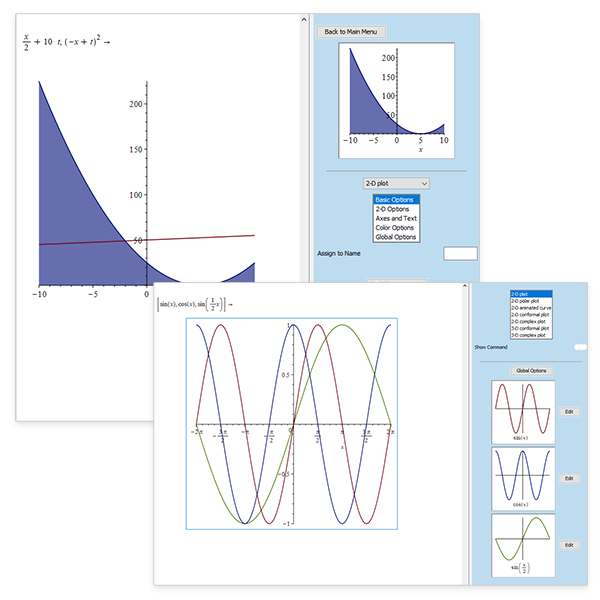
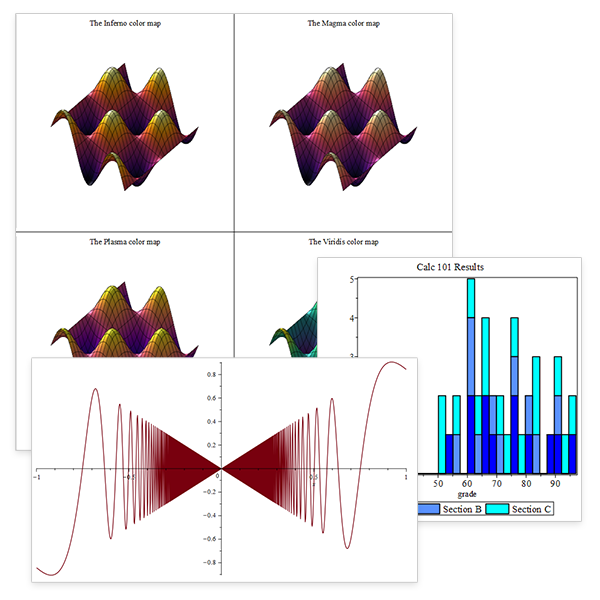
Visualization Made Easier
From automatic detection of discontinuities to increasing the amount of detail when you zoom in, everyday plotting in Maple just got better.
Just Click and Plot
The enhanced Plot Builder makes it even simpler to create illuminating plots and animations, with just a few mouse clicks!
Making Connections
Jupyter® fans can now access the mathematical power of Maple in their Jupyter and JupyterLab notebooks.
If you are trying to decide if you should upgrade to Maple 2022, here are some of our favorite “quality of life” improvements in Maple 2022. If these are features you care about, this list might just make your decision easier! (And if not, there are many, many other improvements and additions to explore.)
Want to see some examples? Watch this video: Should You Upgrade to Maple 2022?